 |
|
| |
|
|
| Slide |
010 |
Interventions for Tuberculosis Control and Elimination |
 |
Next |
 |
 |
Previous |
 |
First |
 |
Last |
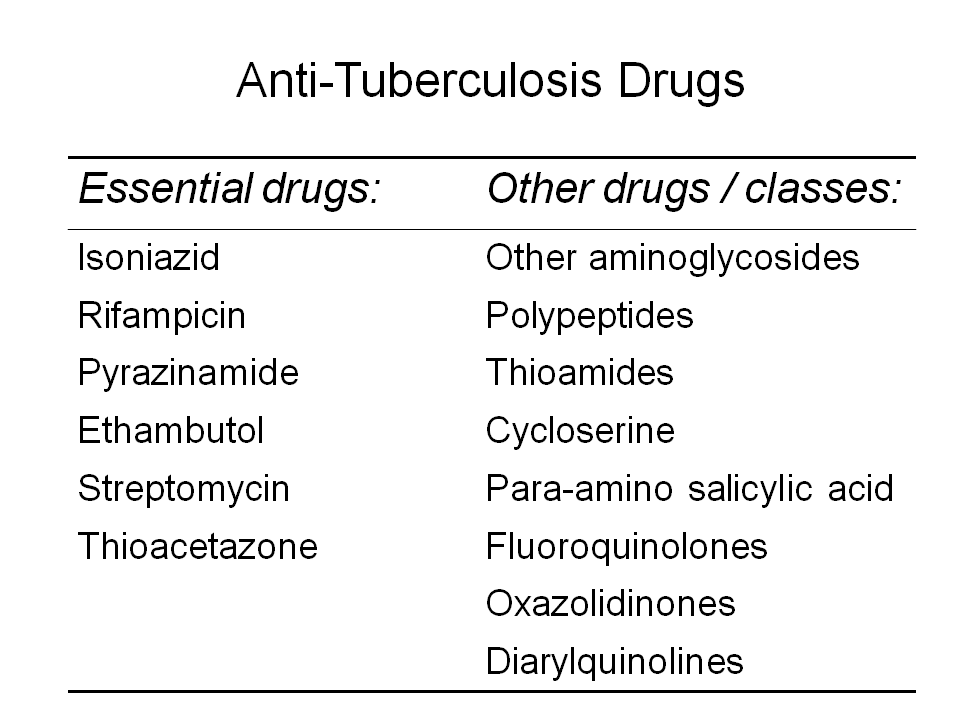
There are six anti-tuberculosis drugs on the Essential Drug List of the World Health Organization: isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, streptomycin, and thioacetazone. Thioacetazone is virtually no more used as a first line drug, but we will briefly discuss it as it played an essential role during the development of the DOTS strategy to ensure "the balance of regimens".
There are other drugs and drug classes that are active against M. tuberculosis. With few exceptions, these often called second-line drugs are more expensive, less efficacious, and poorer tolerated than the first line drugs.
This review will concentrate on the essential drugs. Clinicians as well as public health specialists dealing with tuberculosis should have some basic knowledge about these drugs, including their pharmacokinetics, dosage, adverse drug events, and interactions with other medications. |
| |
|
Go to top
Last update:
September 29, 2010